Content

The Mass Asset Disposals program performs this post automatically unless you specify Batch Approval in your system’s setup. If necessary, you can dispose of a single subledger for one or more assets.
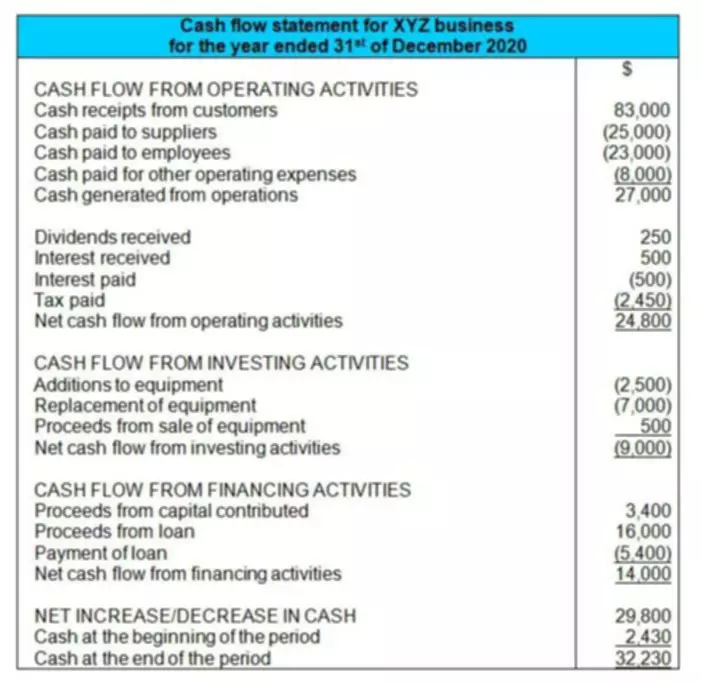
An asset is disposed of when it is no longer needed by a business. Sometimes the business uses up the asset completely, and other times, the asset still has some value and can be sold. When calculating the gain or loss on disposal, we must calculate the asset’s carrying value. In the event of a sale, the fixed assets that have been sold must cease to be included in the assets of the company. The assets of the company must be reduced by the amount of the fixed asset that has been sold. Also, if a company disposes of assets by selling with gain or loss, the gain and loss should be reported on the income statement. CPAs should do this if these gains and losses are not separately presented on the face of the income statement, the caption in the income statement or statement of activities.
Examples of Fixed Asset Disposal Journal Entries
There are four accounts affected when writing off a fixed asset at disposal. When you write something off the books, accounts with normal debit balances are credited and accounts with normal credit balances are debited. Fixed Assets are not revalued unless there has been a significant change in value shortly before they are closed. It is unlikely that the company would sell all of its Fixed Assets before the next revaluation, if they were to be sold and there was no change in value at this point, it how to record disposal of asset could result in a loss on sale of these assets. A company must present a long-lived asset held for sale separately in its financial statements. Major classes of assets and liabilities held for sale must not be offset and presented as one amount, they must be separately disclosed either on the face of the statement itself or in the notes. A company must continue to classify long-lived assets it plans to dispose of by some method other than by sale as held and used until it actually gets rid of them.
- In the first and final years of an asset’s life, the First Year Spread and Last Year Spread will override the disposal rules.
- Consideration received includes all sales posted to the asset’s subaccount and downwards revaluations.
- The following journal entries reduce the asset’s book value to $324,500 (cost of $600,000 less accumulated depreciation of $275,500).
- The edit of the disposal date has been changed in the disposal programs to not force the user to remove the date disposed before disposing an asset.
After five years, the net book value of the tool is $5,000, i.e. $ 10,000 – (5 x $1,000). https://www.bookstime.com/ After 10 years of use, while the tool is considered obsolete, its value is zero.
Why is it necessary to record depreciation on fixed assets?
The fixed asset has no salvage value and it has a useful life of five years. Therefore, the accounting for similar events and circumstances will be the same. Additionally, the information value of reported financial information will be improved. An asset is any resource that you own or manage with the expectation that it will yield continuing benefits or cash flows. An asset is also a resource the value of which you can dependably measure. Entities record their purchase of a fixed asset on the balance sheet, Asset purchases used to be noted on a sources and uses of funds statement, which is now called a cash flow statement.
A Beginner’s Guide to Accumulated Depreciation – The Motley Fool
A Beginner’s Guide to Accumulated Depreciation.
Posted: Wed, 18 May 2022 07:00:00 GMT [source]
